 Webinar – Yığın Malzeme Taşımacılığı Bilimine Giriş
Webinar – Yığın Malzeme Taşımacılığı Bilimine Giriş
Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry is driven by two key strategies, namely reducing costs or incorporating new technologies.
Examples of those key strategies include Process Analytical Technology (PAT), and new drug delivery systems.
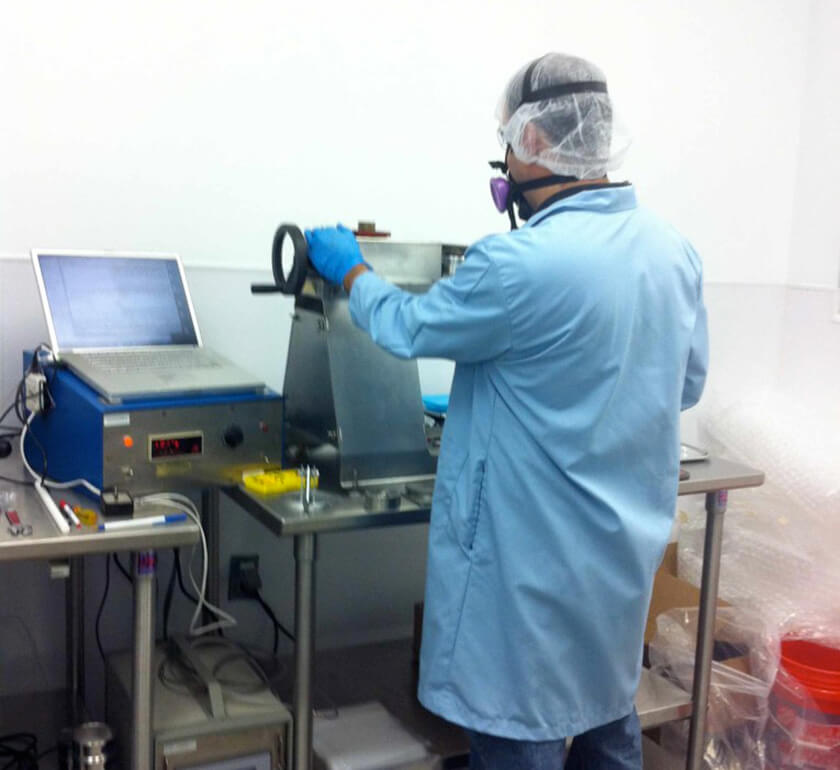
Reducing costs may require the use of new raw material suppliers, which could result in unplanned process variability or unanticipated process changes. Perhaps you are on the other side of this relationship, whereby you are unsure if your process changes will affect your customer. On the other hand, newer materials and manufacturing techniques demand a better understanding of the process as a whole. This may include implementing various programs such as six sigma, PAT, quality-by-design (QBD), or specific FDA guidance documents, with the goal of improved quality and reduced time-to-market. Novel techniques (e.g., continuous blending) in the pharmaceutical industry can pose increased risk and effort to implement.

Medicinal capsules on a tray.
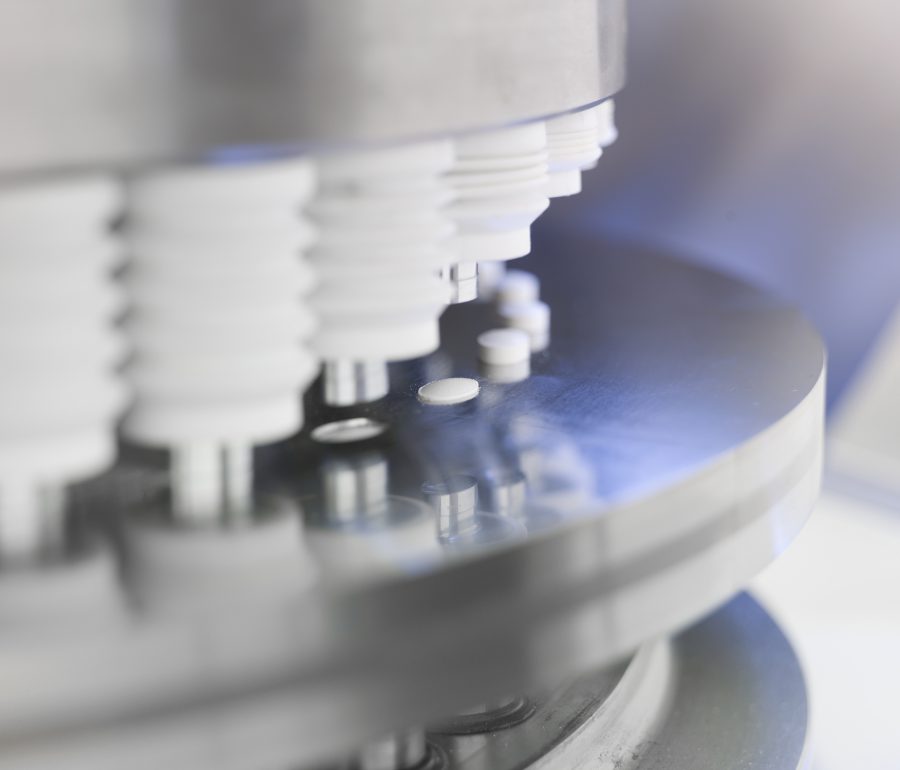
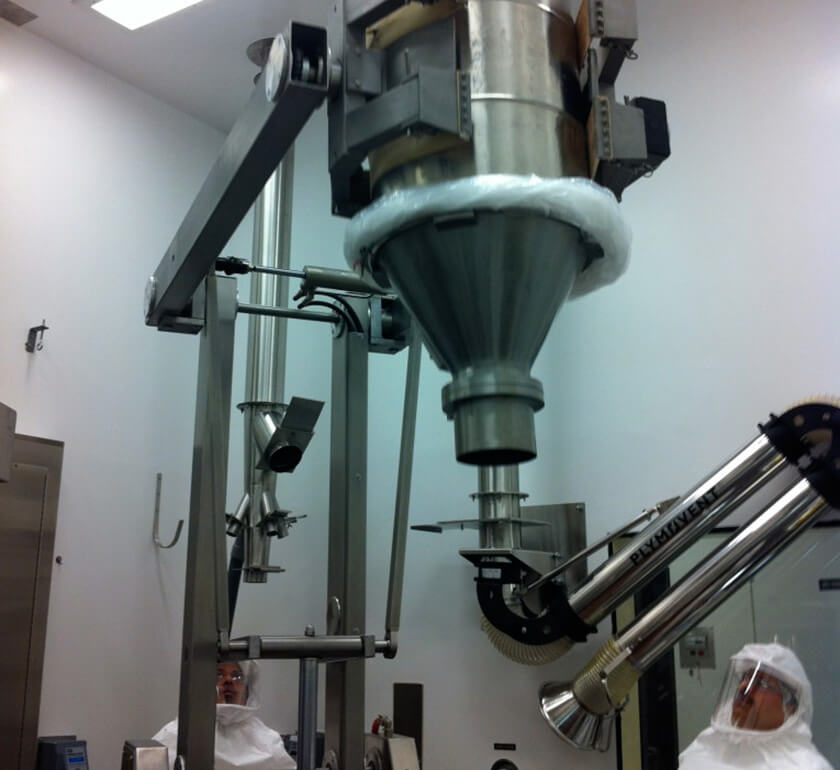
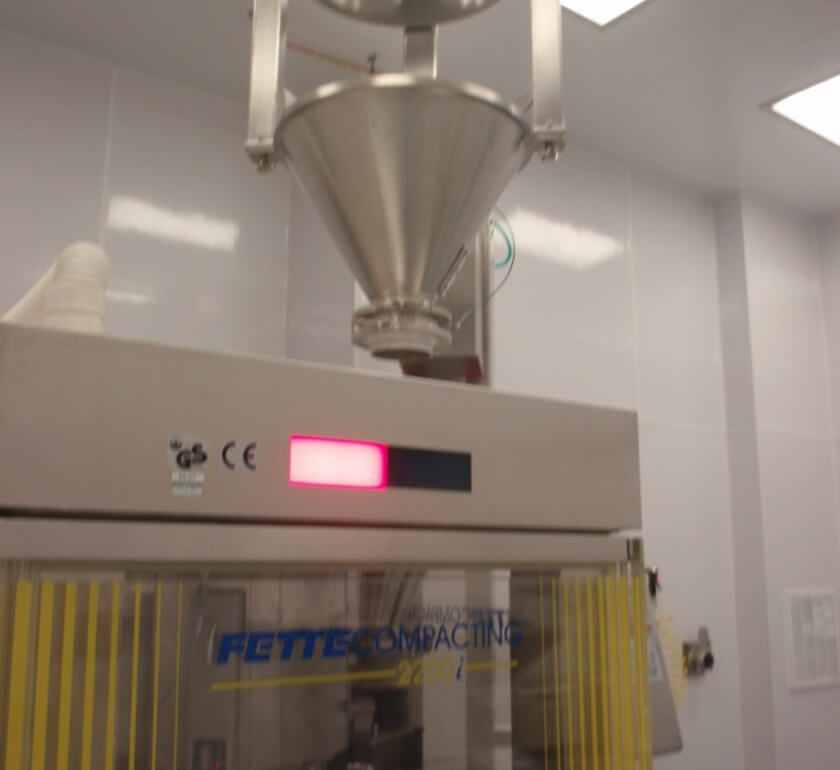
Tabletting press
Pharmaceutical products.
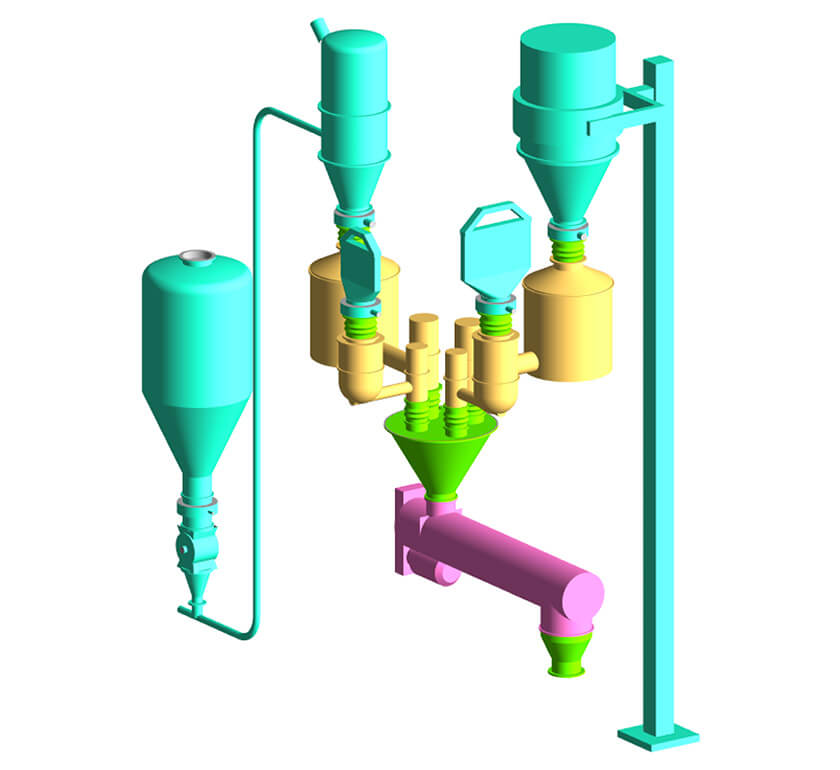
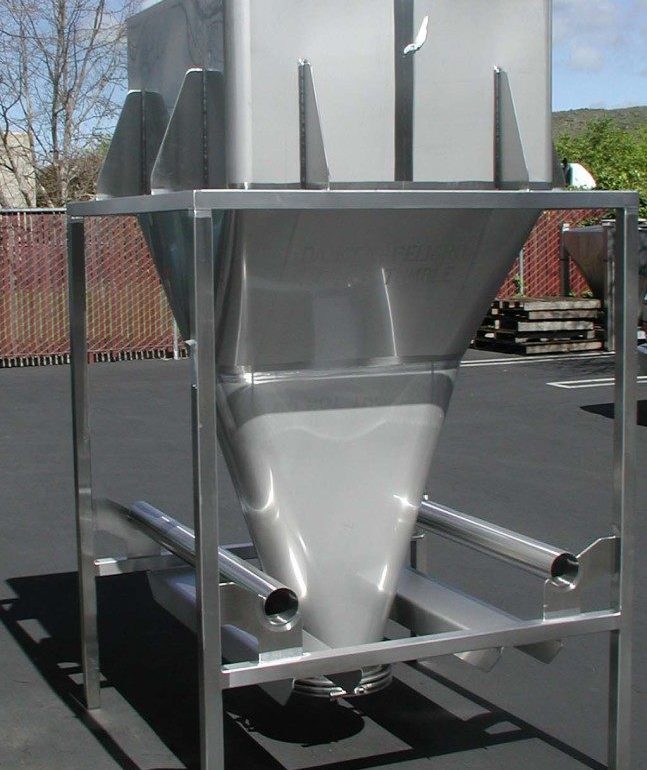
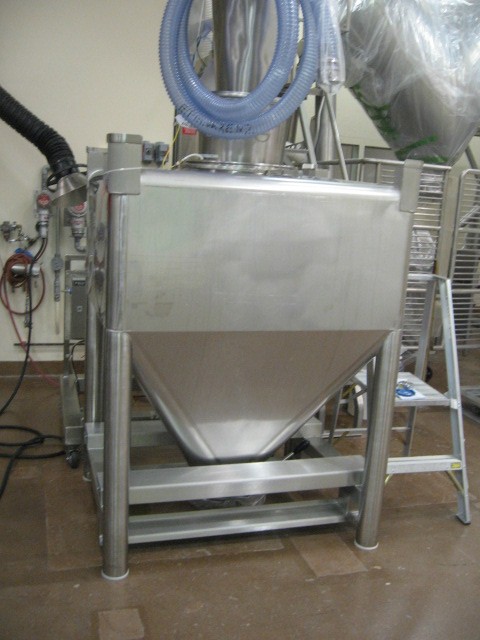
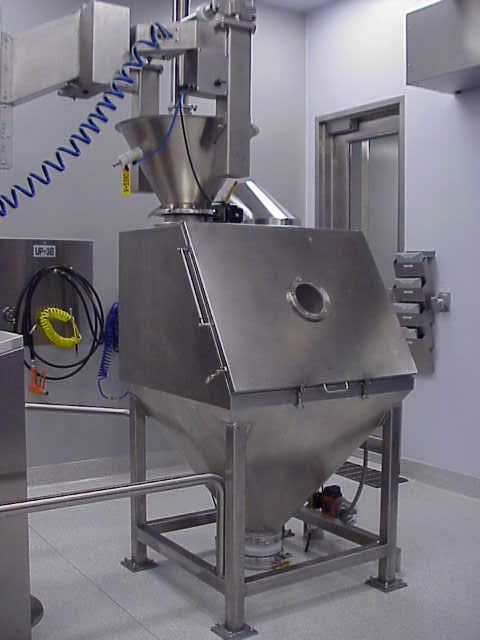
Material handling considerations for a continuous manufacturing line.















