What Are Segregation & Blending?
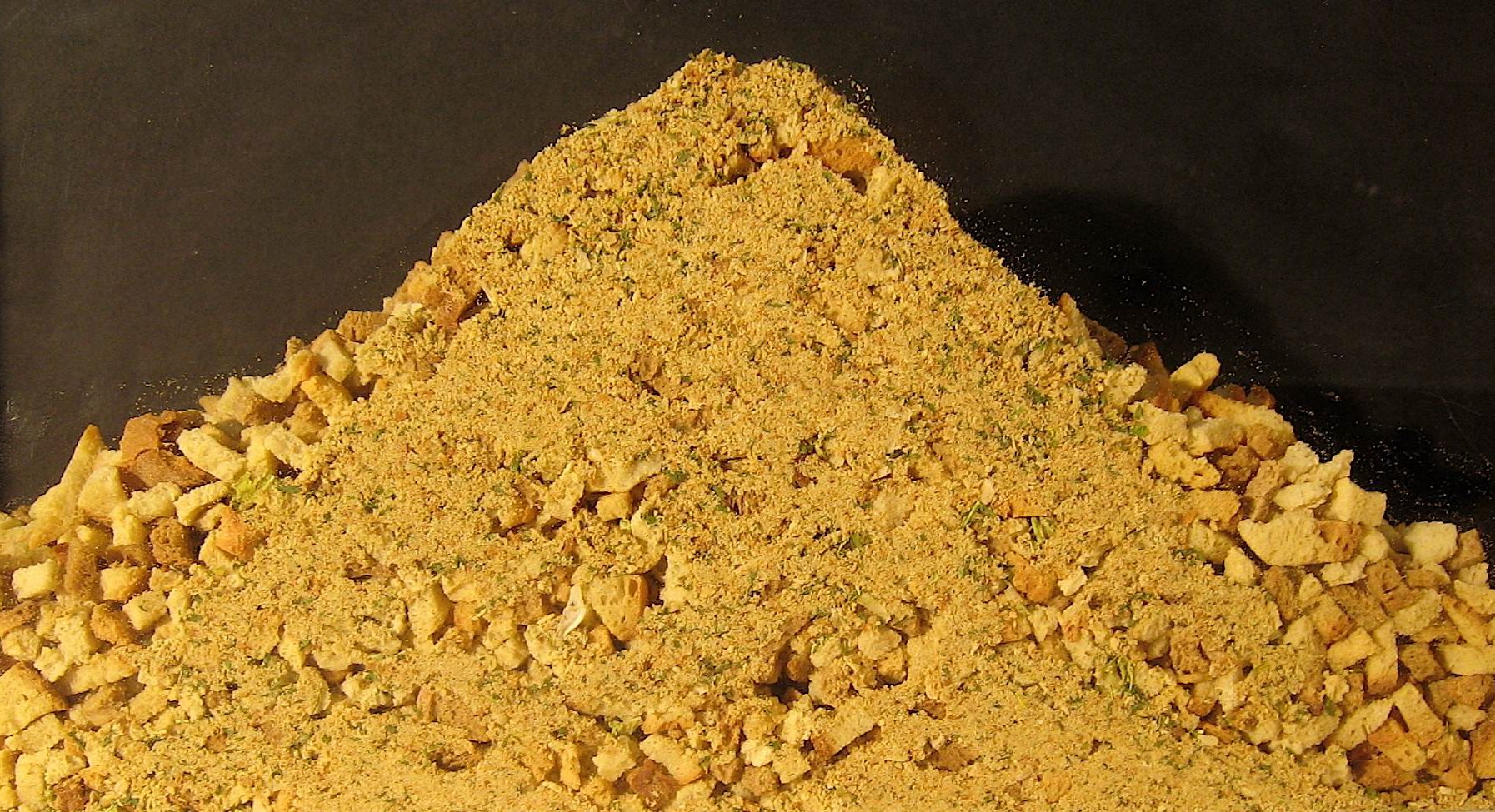
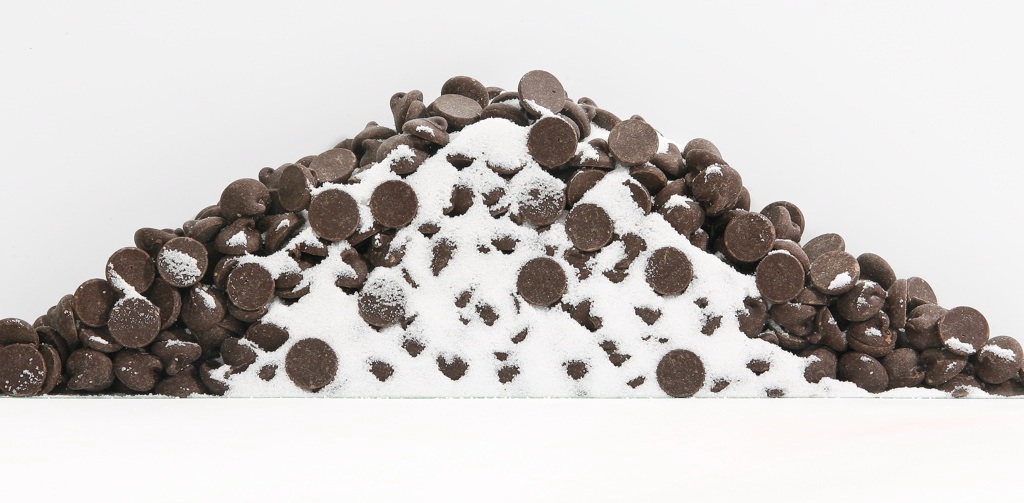
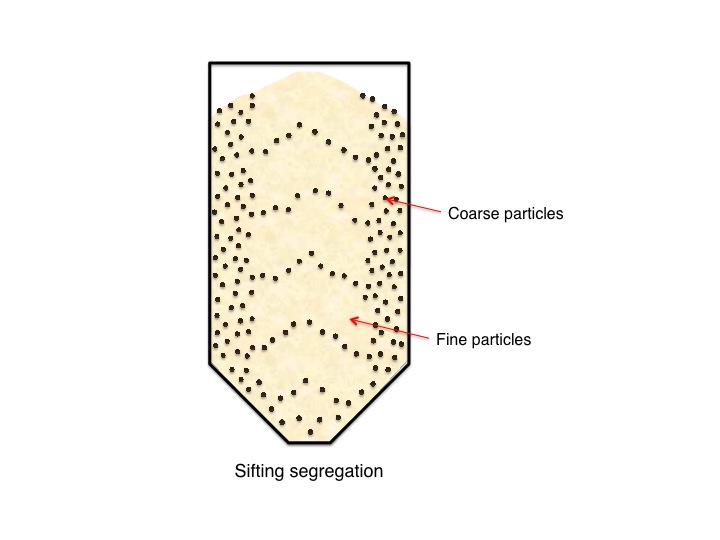
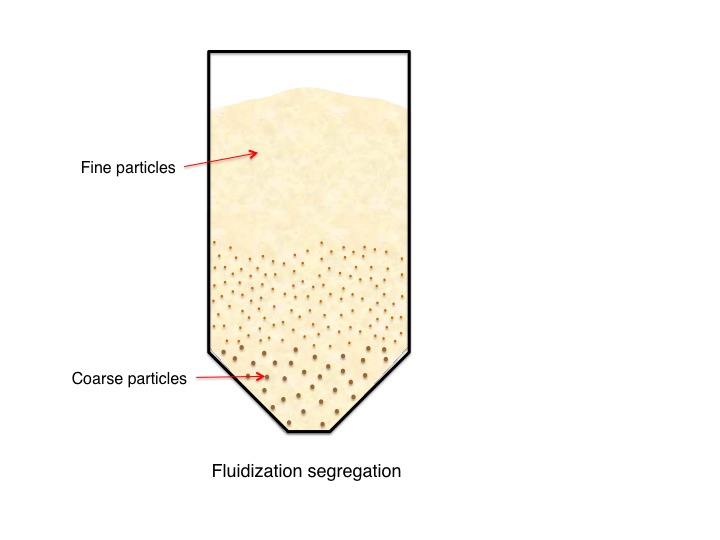
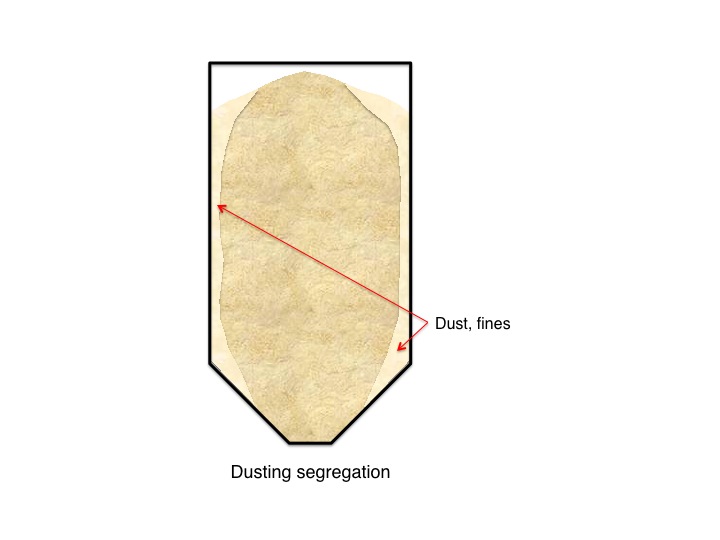
Segregation results when particles separate due to differences in their size, shape, or density. It commonly happens when handling a powder blend or material with varied particle size. Common segregation mechanisms include sifting, fluidization, and dusting.
Blending (or mixing) is the opposite behavior of segregation. The process of blending occurs when a collection of particles is homogenized or multiple ingredients are mixed to obtain a uniform product. Some materials require gentle tumble blending in a controlled batch mode while others require high shear to continuously blend highly cohesive and tough-to-mix ingredients. A well-blended material does not guarantee production of a quality product due to segregation effects that may result during powder flow.
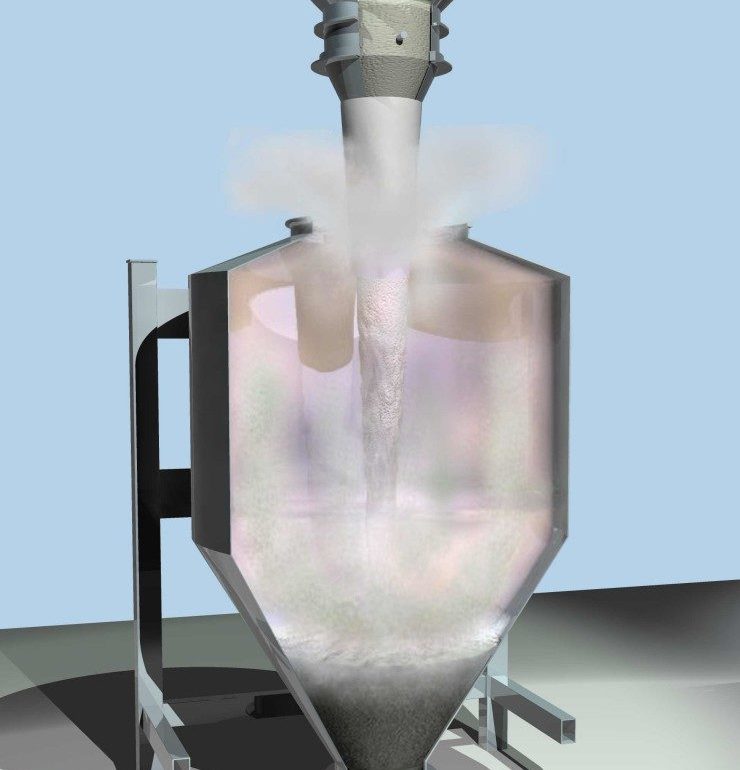
Dusting and segregation during the filling of a bin.
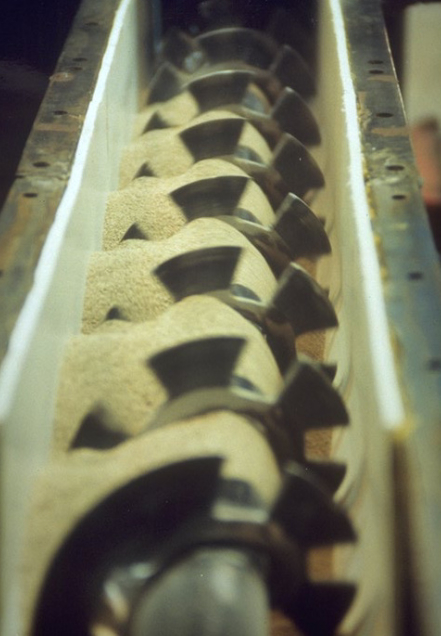

Blending and mixing screw.
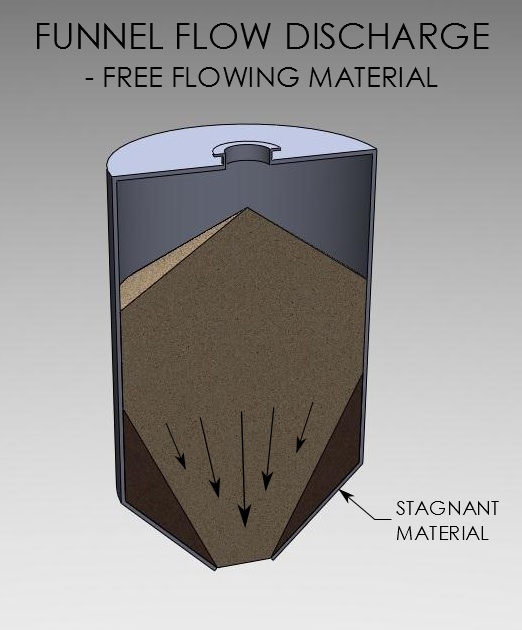
Funnel flow is a flow pattern in which solid flows in a channel formed within stagnant material.
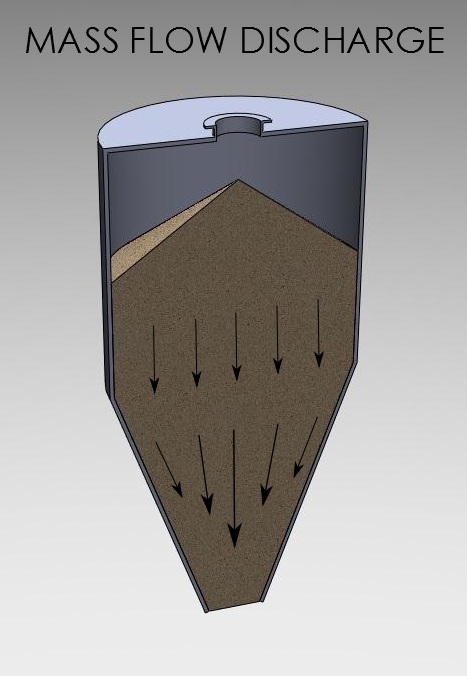
Mass flow is a flow pattern in which all solid in a bin is in motion whenever any of it is withdrawn.
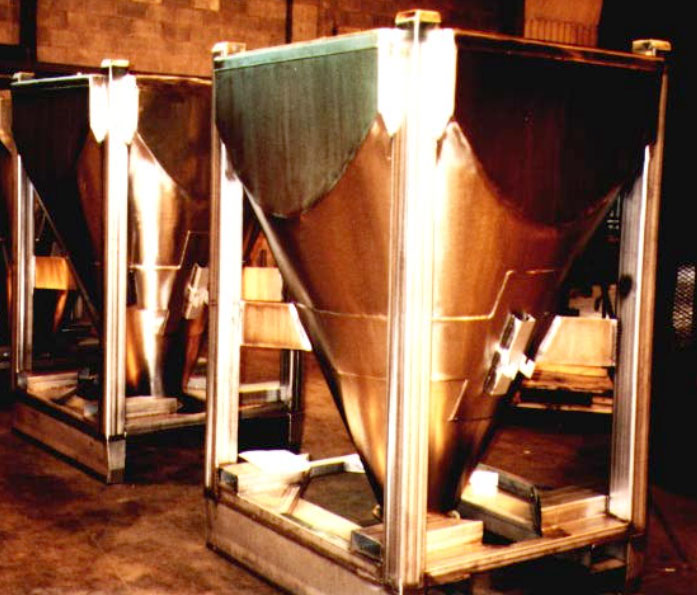

Mass flow bins.
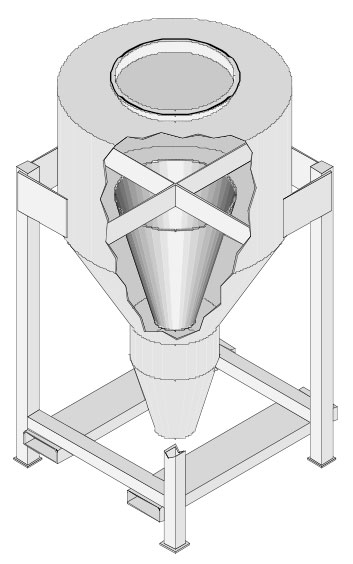
Mass flow binsert portable container.
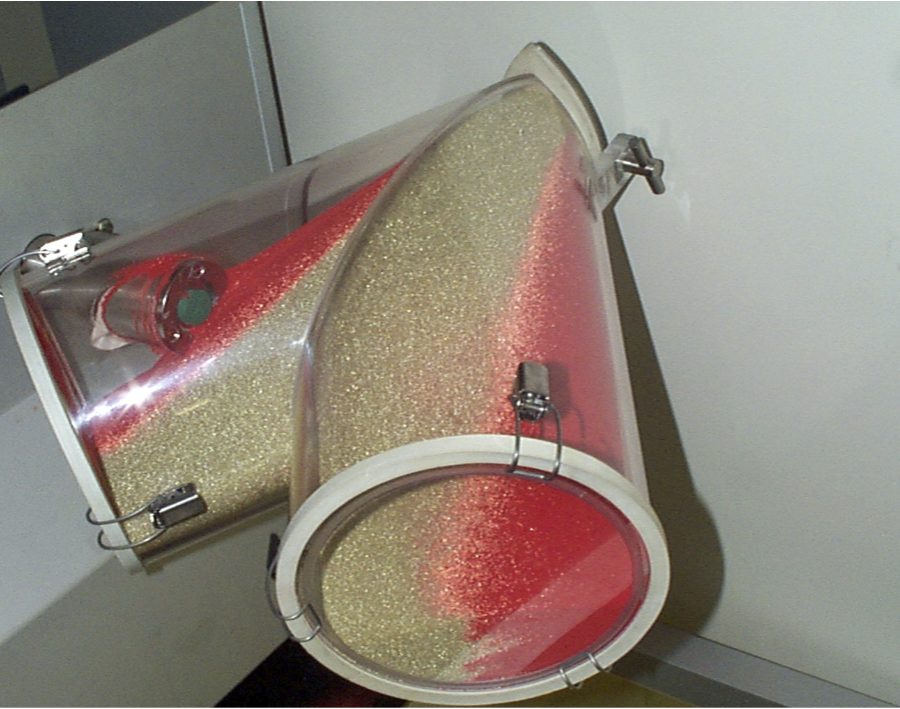

Pellet segregation in V-blender.