Webinar – Yığın Malzeme Taşımacılığı Bilimine Giriş
Webinar – Yığın Malzeme Taşımacılığı Bilimine Giriş
Moisture Migration & Caking Analysis
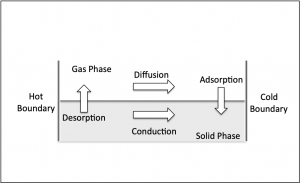
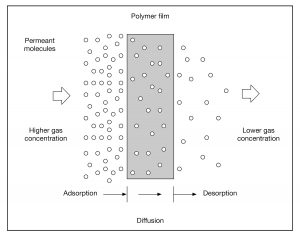
Caking results when particles agglomerate and form solid lumps or masses. Typically caking is undesirable, resulting in customer complaints, rejected product, and additional processing steps needed to delump the material. Though caking commonly occurs with many packaged powders, it can also occur in poorly designed silos, hoppers, and other equipment that allows material stagnation. Preventing caking can be difficult if factors contributing to these problems are not well-understood. Key factors affecting caking are intrinsic properties and environmental conditions. Caking induced by moisture is the most common cause.
Modeling Moisture Migration and Caking is an efficient way to test conditions rapidly without having to stop production or wait for expensive stoppages due to agglomeration.
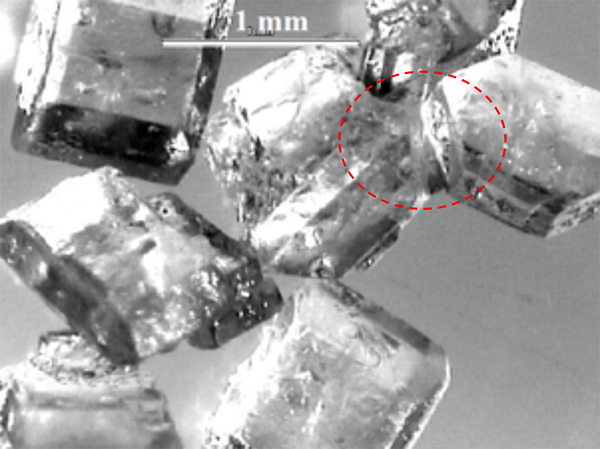
Crystals lumping together and building a bridge, leading to caking of the material.
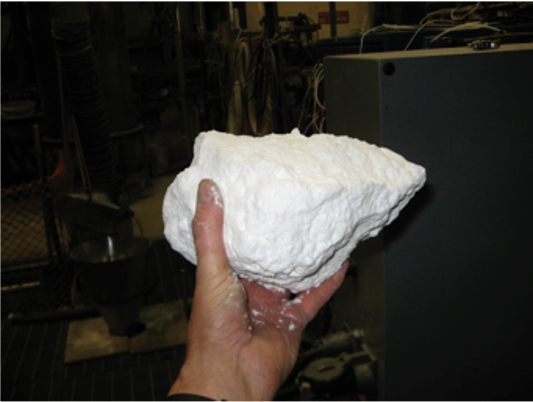

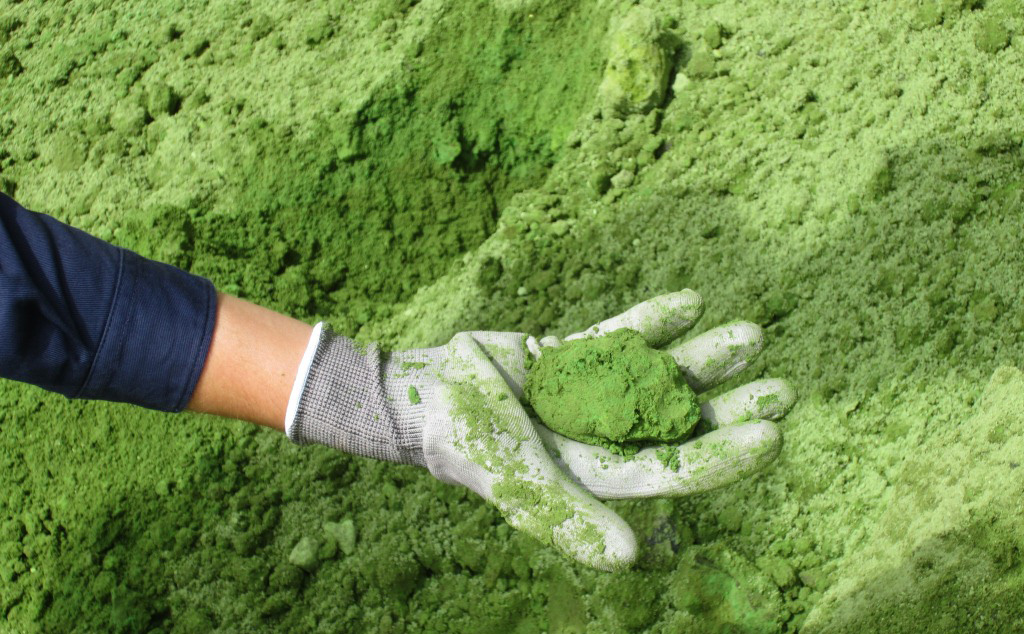
Caking of powdered material.